No products in the basket.
- Latest
- Trending
Indonesia’s parliament has approved the country’s membership in the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) trade pact and becomes the latest country in ASEAN to join in what is the world’s largest free trade agreement.
The RCEP is estimated to cover 30 percent of the global GDP of US$25.8 trillion, and comprise 30 percent of the world’s population.
While Indonesian exports will benefit from the reduction in tariffs between RCEP members, the country’s downstream industries are also well poised to receive greater investments. Supported by an abundance of natural resources, Indonesia is actively seeking to climb up the global value chain – transitioning from an exporter of raw commodities to a producer of high-value products.
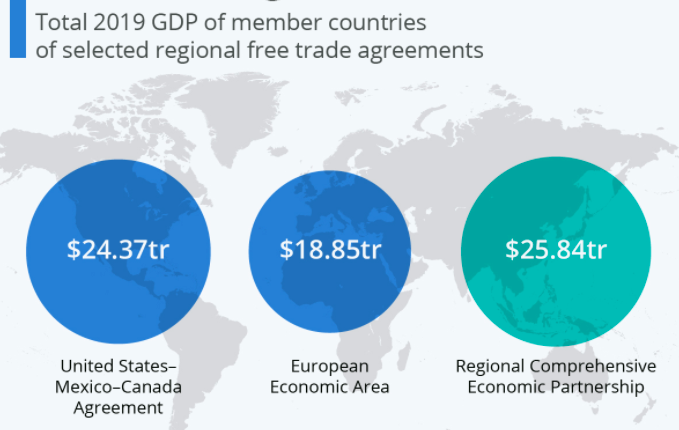
Indonesia, Southeast Asia’s largest economy, ratified its membership in the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) on August 30, 2022, and becomes the latest country in ASEAN to ratify this trade agreement. The RCEP is estimated to cover 30 percent of the global GDP of US$25.8 trillion, and comprise 30 percent of the world’s population.
With the RCEP set to eliminate 92 percent of tariffs on goods traded among its 15 members, Indonesian lawmakers have expressed concerns that this could trigger an influx of imported goods and thus impact the competitiveness of local businesses, particularly micro and small medium enterprises (MSME). However, with President Joko Widodo’s coalition controlling 80 percent of parliament, ratification of the RCEP is only a matter of time.

Indonesia’s Chief Economics Minister, Airlangga Hartarto, expects the country to book a trade deficit in the early period after implementation, but by 2040, the RCEP could boost the country’s trade surplus by US$979 million, more than double the current trade surplus of US$383 million. Further, Indonesia could see GDP growth by 0.07 percentage points and an increase in exports and imports by US$5 billion and US$4 billion, respectively.
The country’s protectionist policies have made it difficult for foreign investments to enter the country. Indonesia struggled to capture a significant share of the investment and production from businesses moving out of China due to the US-China trade war.
The government has since introduced the Omnibus Law in late 2020 which removes bureaucratic inefficiencies, simplifies business licensing requirements, and liberalized more industries to attract foreign investments.
Importantly for Indonesia, the RCEP presents an opportunity to better integrate Indonesia into regional value chains and attract investments into its industries, especially manufacturing, which accounts for 20 percent of GDP. The government aims for Indonesia to become a manufacturing hub that rivals Germany and South Korea.
Indonesia’s main areas of production are textiles and garments, electronics, automotive, footwear, food and beverages, and chemicals. The country’s trade-to-GDP ratio is 40 percent, lower than the global average of 55 to 60 percent, highlighting that Indonesia is poorly integrated with global supply and value chains.
During the 1990s, Indonesia saw large-scale industrialization due to deregulation and a policy shift towards export-oriented industries. However, the country was slow in accumulating technology and reskilling its human resources, leading it to fall behind in its manufacturing competitiveness compared to Singapore, Malaysia, and Thailand.
Indonesia’s strength lies in its extensive natural resources and the processing industries associated with them. Membership in the RCEP can incentivize new investments and partnerships to obtain the technology and resources for expanding industrial capabilities and promoting innovation, besides enabling the climb up the value chain.
Indonesia is keen to diversify its manufacturing sector and the RCEP can help transform the country into a producer of high-value products. Incubating new and emerging value chains will be vital if the country wants to increase the contribution of the manufacturing sector to GDP to 25 percent from 20 percent by 2030.
One such example of an emerging value chain the country is exploring is the establishment of an electric vehicle battery plant – the first in Southeast Asia — and marking a milestone in the country’s drive to becoming a global EV battery supplier and establishing a comprehensive EV supply chain.
Indonesia has significant nickel reserves – approximately 24 percent of the world’s reserves – and is a vital component of EV batteries. Moreover, the country’s Grasberg mine located in Papua province, has the second-largest reserve of copper in the world, another key component of EV batteries. When fully operational in 2023, the plant is expected to produce 10-gigawatt hours of lithium-ion battery cells for 150,000 EVs.
Read the complete article here :
Indonesia Ratifies RCEP Trade Agreement (aseanbriefing.com)
ASEAN Briefing features business news, regulatory updates and extensive data on ASEAN free trade, double tax agreements and foreign direct investment laws in the region. Covering all ASEAN members (Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam)








